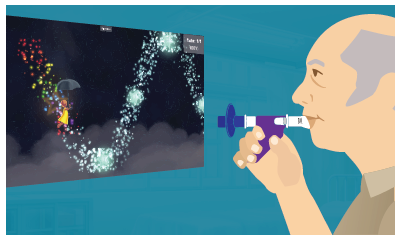
This 66-year-old gentleman was referred to a skilled nursing facility for rehabilitation services due to right-sided weakness and general debility. He was hospitalized after a stroke which required thrombectomy (procedure to remove blood clot). Prior to his stroke, he was living with his spouse in a home with a 3-step entry, was independent with all functional mobility, and walked with a rolling walker.
Decreasing Pain and Improving Functional Mobility
Topics: Patient Success Story, Neuro Rehab
Dementia Care With Advanced Rehab Technology: Goal-Oriented Activity
As dementia progresses, the ability to think clearly and function independently becomes impaired. Traditional therapy becomes increasingly difficult in this population and goal-oriented rehab with biofeedback may be a key factor in improving function.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
A skilled nursing facility rehab department incorporated the OmniVR® for residents in their memory care unit as a way to make activities interactive and fun. Therapists note it is typically difficult to engage these and similar residents in activities, sustain their attention, and keep them actively involved.
Topics: Patient Success Story, Neuro Rehab
Dementia Care With Advanced Rehabilitation Technology: Exercise
According to the CDC, dementia affects one’s ability to remember, think, and make decisions that impact daily activities and safety. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common type of dementia accounting for 60-80% of cases. As dementia progresses to increased levels of memory loss and confusion, the individual becomes more sedentary and frail. Rehabilitation in this population should be tailored to patient needs addressing cognition, strength, gait, balance, endurance, and function.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Interventions for Individuals with Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder often requiring therapy to address motor symptoms such as bradykinesia, rigidity, tremors, shuffling and freezing gait, poor postural control, and impaired balance. Exercise plays a key role in rehabilitation for this population with additional benefits being achieved by incorporating biophysical agents and advanced technologies. Research demonstrates that exercise improves motor skill performance, which may be enhanced with cognitive engagement through feedback, cueing, dual-tasking training, and motivation (Petzinger, et al., 2013).
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Rehabilitation of Individuals Post-Stroke
According to the CDC, each year in the United States more than 795,000 people suffer a stroke and it is the leading cause of serious long-term disability. Individuals who suffer a stroke may have muscle weakness throughout the body including muscles of respiration and swallowing. They also may have compromised endurance, poor balance, and increased dependency with mobility and activities of daily living which greatly impact their quality of life.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Improving Strength and Functional Mobility with Electrical Stimulation and Exercise
Patient Information: Male, Age 75
Topics: Patient Success Story, Neuro Rehab
Cycling Exercise in Rehabilitation to Improve Coordination and Normalize Muscle Tone
Physical and occupational therapists treat many individuals who present with impaired coordination, motor control, balance and tone. These individuals may have a wide range of diagnoses, from neurologically involved, such as cerebral vascular accident (CVA) and Parkinson’s disease, to orthopedic involvement such as post-total knee replacement (TKR). The common goal of improving functional mobility and outcomes may be achieved by the addition of research-supported cycling and biophysical agents.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary, Neuro Rehab
Improving Functional Mobility Using Electrical Stimulation, Virtual Reality, and Exercise
Patient Information: Male, Age 79
Diagnosis: Right Ankle Fracture / Gastrointestinal (GI) bleed
History: This gentleman was referred to a skilled nursing facility for rehabilitation services due to weakness and reduced functional mobility after hospitalization for a right ankle fracture (from a fall) and a GI bleed. Prior to hospitalization, he used a rolling walker to ambulate and lived in a 2-story home with a roommate who helped with household tasks.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Patient Success Story, Neuro Rehab
Over the past several years, the body of evidence on the effectiveness of virtual reality (VR) in rehabilitation has significantly expanded. VR has been studied for a variety of diagnoses including stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, dementia, burns, pain, and total knee arthroplasty. VR helps enhance patient involvement and motivation while increasing the repetitions and duration of exercise. Benefits addressing ADL performance, balance, gait, pain, and cognition have been reported.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Pain Management, Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary, Orthopedic, Neuro Rehab