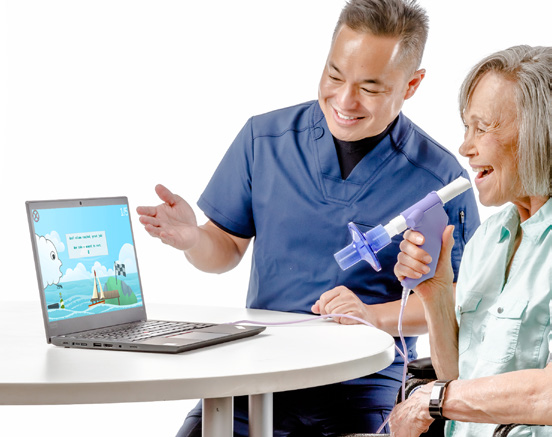
This 71-year-old woman was referred to a skilled nursing facility for rehabilitation services due to requiring increased assistance with all functional tasks after a five-day hospitalization due to nine falls in one week and diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Prior to hospitalization she lived with her grandchildren in a single story home with four steps at the entry and was independent with ambulation and all functional activities including meal prep.
Improving Balance and Functional Mobility
Fall Prevention Using Virtual Reality (VR) for Breathing and Balance Exercises
According to the CDC, more than 25% of older adults fall each year. Muscle strength and balance decline with aging which can lead to falls and diminished quality of life.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
Addressing Frailty with Advanced Rehab Technology
Aging results in a loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia) and a decrease in muscle strength, which can lead to functional impairment and frailty. Research highlights the impact of frailty on individuals and how exercise and rehab technology may counteract this decline.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Virtual Reality in Fall Prevention
According to the CDC, more than one in four older adults fall each year. Falls may lead to fear of falling, decreased mobility, dependence, increased risk of future falls, and even death. The goal of a fall prevention and balance program is to decrease future falls and improve functional mobility, safety, and quality of life. Rehabilitation for those at risk of falling may include training for static and dynamic balance, gait, dual-task (DT) activity, and cognition which may be accomplished with virtual reality.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
Pain*
Is your resident experiencing pain?
• Always assess pain level
• If resident is in pain, report immediately
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance
Interdisciplinary Fall Prevention for Geriatrics
In a recent CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, Moreland & Lee (2021) analyzed 2018 U.S. data which revealed individuals 65 and older had 2.4 million emergency department visits and more than 700,000 hospitalizations due to unintentional injuries. Greater than 90% of these injuries were related to falls. This shows the importance of an effective interdisciplinary fall prevention and balance program for the geriatric population.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
Decreasing Pain and Improving Mobility Using Diathermy and Exercise
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Pain Management, Patient Success Story
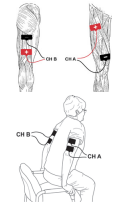
Objective Tests and Measures: Strength Assessment and Treatment Guidance
Muscle strength decline is associated with normal aging and may be accelerated by illness, disease, or injury. Decreased physical activity resulting from COVID-19 mitigation efforts is exacerbating the incidence of muscle disuse atrophy in older adults. Strength declines may lead to functional and mobility deficits with increased risk of falls, injury, or death. According to the CDC, each year three million adults are treated in emergency departments for injuries related to falls. By 2030 fall deaths are anticipated to rise to seven per hour. Accurate assessment of strength using validated tests and objective measures is crucial to creating an appropriate treatment plan and achieving outcomes that reduce fall risk.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
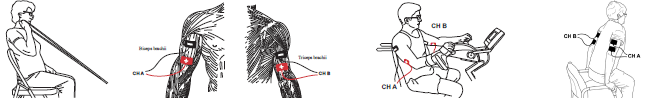
Improving Functional Mobility Using Electrical Stimulation, Virtual Reality, and Exercise
Patient Information: Male, Age 79
Diagnosis: Right Ankle Fracture / Gastrointestinal (GI) bleed
History: This gentleman was referred to a skilled nursing facility for rehabilitation services due to weakness and reduced functional mobility after hospitalization for a right ankle fracture (from a fall) and a GI bleed. Prior to hospitalization, he used a rolling walker to ambulate and lived in a 2-story home with a roommate who helped with household tasks.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Patient Success Story, Neuro Rehab
Over the past several years, the body of evidence on the effectiveness of virtual reality (VR) in rehabilitation has significantly expanded. VR has been studied for a variety of diagnoses including stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, dementia, burns, pain, and total knee arthroplasty. VR helps enhance patient involvement and motivation while increasing the repetitions and duration of exercise. Benefits addressing ADL performance, balance, gait, pain, and cognition have been reported.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Pain Management, Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary, Orthopedic, Neuro Rehab