Breathing impacts everything we do from bed mobility, transfers and gait to ADLs and IADLs. Incorporating patient-specific breathing strategies into a comprehensive rehab program not only addresses breathing impairment due to cardiopulmonary compromise, but also positively impacts pain, balance, function, and ADL performance.
Breathing Exercise Improves ADLs, Core Stability, and Pain
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Cardiac Management Including Advanced Rehab Technology
According to the CDC, coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease in the US. It is caused by plaque build-up in the coronary arteries which slows blood flow. The most common symptom of CAD is chest pain. However, many people don’t have symptoms and only find out they have CAD after they suffer a heart attack.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
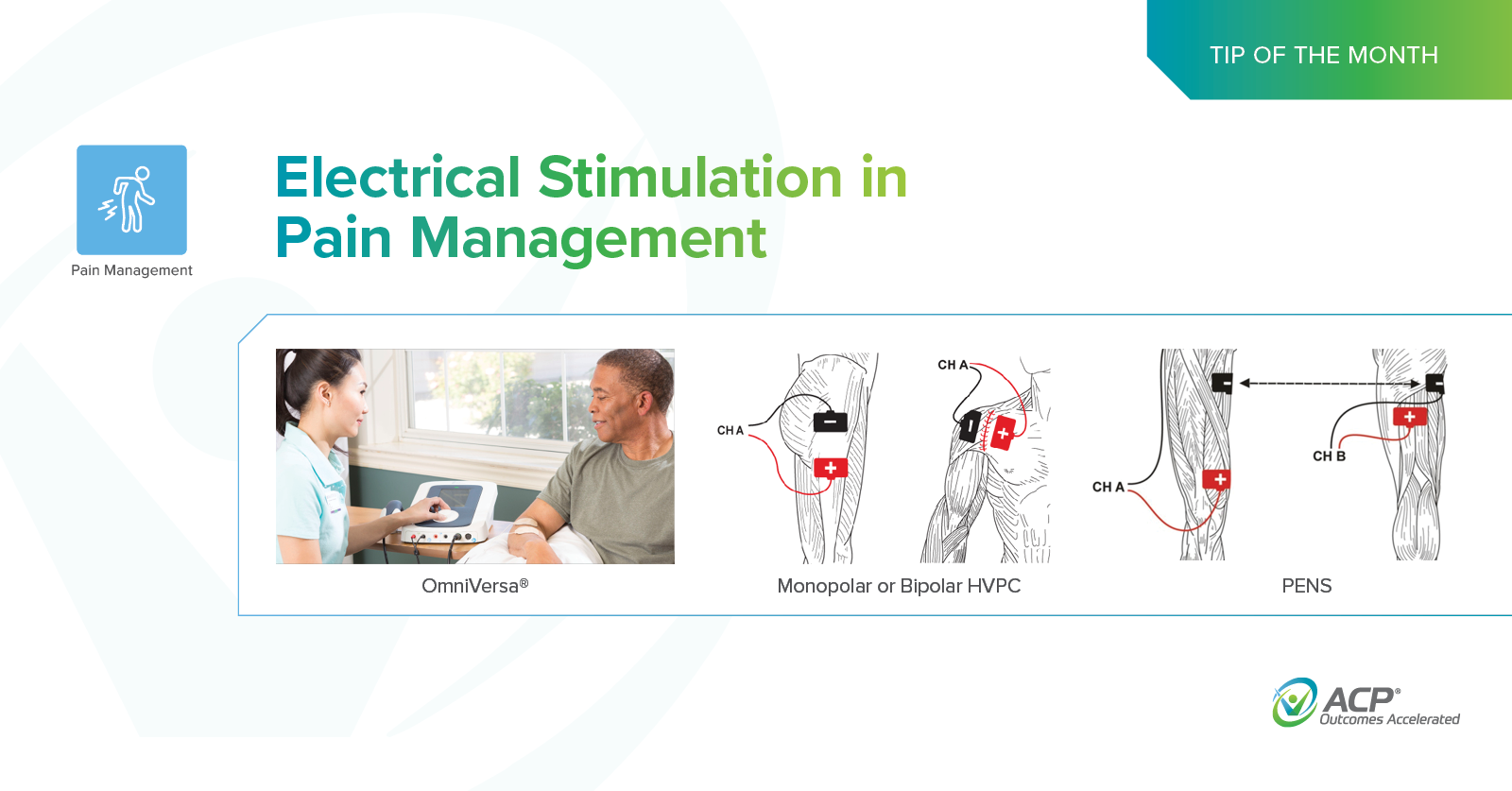
Electrical Stimulation in Pain Management
Pain is common in the geriatric population leading to a rapid decline in cognition and function with the eventual need for assistance and potential institutionalization. While opioids are often used to treat pain, their side effects are now well established. In therapy, multimodal non-pharmacologic pain management interventions are effective at improving clinical outcomes.
Topics: Pain Management, Clinical Tip
Dementia Care With Advanced Rehab Technology: Goal-Oriented Activity
As dementia progresses, the ability to think clearly and function independently becomes impaired. Traditional therapy becomes increasingly difficult in this population and goal-oriented rehab with biofeedback may be a key factor in improving function.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Fall Prevention Using Virtual Reality (VR) for Breathing and Balance Exercises
According to the CDC, more than 25% of older adults fall each year. Muscle strength and balance decline with aging which can lead to falls and diminished quality of life.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
Effective Alternatives for Pain Management Using Virtual Reality and Breathing Therapy
Acute and chronic pain are prevalent in the United States and can affect an individual’s mobility, function, and independence. According to the CDC, approximately 20% of the adult population suffers from chronic pain. Opioids including oxycodone, tramadol, and fentanyl are among medications often taken for acute and chronic pain. However, opioids have numerous side-effects, are highly addictive, and can lead to overdose and death. Non-pharmacologic alternatives are recommended to address pain and can play a role during the weaning process from opioids.
Topics: Pain Management, Clinical Tip
Improving ADLs in Chronic Conditions
According to the CDC, 78% of adults over 55 in the U.S. have one or more chronic conditions. The ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) such as transfers, dressing, and bathing along with instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) such as shopping, cooking, and cleaning informs healthcare professionals regarding the individual’s level of independence. With chronic conditions such as COPD, chronic heart failure, stroke, and diabetes, individuals may have dyspnea, weakness, and poor aerobic capacity which in turn may lead to impaired ability to perform ADLs and IADLs.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
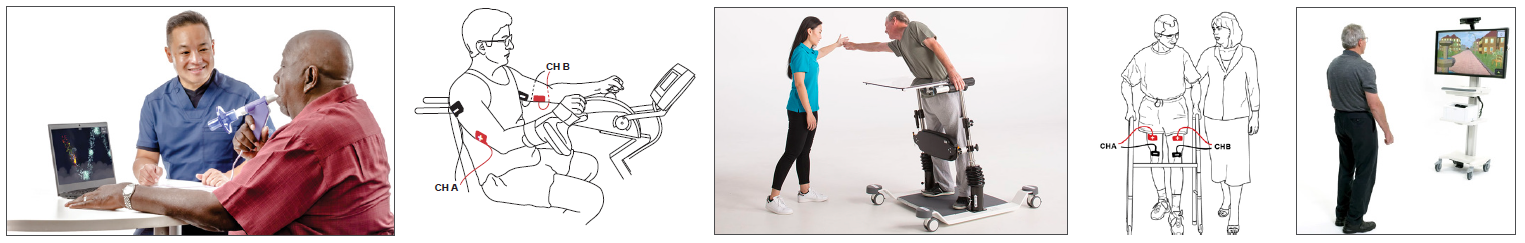
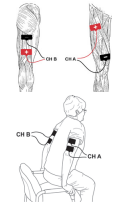
Addressing Frailty with Advanced Rehab Technology
Aging results in a loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia) and a decrease in muscle strength, which can lead to functional impairment and frailty. Research highlights the impact of frailty on individuals and how exercise and rehab technology may counteract this decline.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Ventilatory Strategies for Cardiopulmonary Conditions
Individuals with cardiopulmonary conditions often present with dyspnea, severe weakness, poor endurance, limited mobility, and decreased activity tolerance. As their disease state progresses, their ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) declines, ultimately leading to a loss of independence. A therapy plan of care that includes breathing exercises, energy conservation techniques (e.g., paced activity, assistive device, task planning), and ventilatory strategies may improve the individual’s breathing and functional performance as well as help maintain independence.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
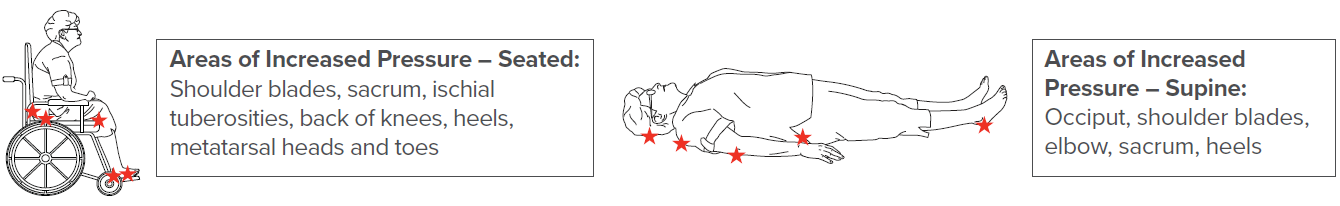
Comprehensive Approach to Wound Healing
Wounds are typically managed with standard nursing care including maintaining a clean wound bed and appropriate dressings and medications. Therapeutic interventions including biophysical agents can be used to directly facilitate and accelerate wound healing. Factors such as pressure, pain, and contracture may delay wound progression or cause wounds to reoccur. Addressing these adjunctive factors related to the wound provides the best overall approach to wound management and limits the risk of reoccurrence.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Wound Management





.png)
_cropped.png)