According to the CDC, each year in the United States more than 795,000 people suffer a stroke and it is the leading cause of serious long-term disability. Individuals who suffer a stroke may have muscle weakness throughout the body including muscles of respiration and swallowing. They also may have compromised endurance, poor balance, and increased dependency with mobility and activities of daily living which greatly impact their quality of life.
Research supports the addition of biophysical agents and advanced rehab technologies as part of a rehabilitation program in the treatment of individuals post-stroke.
- Respiratory muscle training is effective in improving pulmonary function parameters, strength of expiratory and inspiratory muscles, and walking ability (Pozuelo-Carrascosa et al., 2020).
- Effortful swallows increase muscle activity during swallowing providing physiologic benefit in dysphagia exercise, and the addition of sEMG biofeedback enhances performance (Archer et al., 2021).
- Ergometer training can support motor recovery after stroke and is more efficient when assisted with neuromuscular functional electrical stimulation than ergometer training alone (Veldema & Jansen, 2019).
- Virtual reality reinforced biofeedback combined with conventional rehab promotes better outcomes for upper limbs than conventional rehabilitation, regardless of the stroke etiology. (Kiper et al., 2018)
- Functional electrical stimulation combined with standing frame could be useful in improving balance in subacute stroke patients (Lee et al., 2019).
- Clinical practice guidelines for the use of AFO and FES post stroke recommends AFO or FES for individuals with decreased lower extremity motor control who have goals to improve gait speed (Johnston et al., 2021).
ACP’s Biophysical Agents and Advanced Technologies may be an integral part of a comprehensive interdisciplinary neuro rehabilitation program in the treatment of patients post-stroke.
|
OmniFlow® may be beneficial in respiratory and expiratory breathing therapy |
OmnisEMG™ may be beneficial in oral motor strengthening and swallowing therapy |
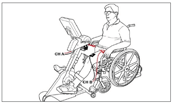
OmniCycle® may be beneficial for strengthening and aerobic capacity training with/without the ability to actively participate on both sides |
|
OmniVR® (sitting ,standing or with OmniStand®) may be beneficial in improving strength, coordination, balance, and cognition |
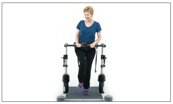
OmniStand® may be beneficial in improving balance and standing endurance |
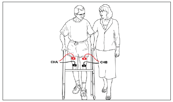
Patterned Electrical Neuromuscular Stimulation (PENS) walk protocol may be beneficial in improving walking pattern, distance, and speed |
References:
Archer, S. K., Smith, C. H., & Newham, D. J. (2021). Surface Electromyographic Biofeedback and the Effortful Swallow Exercise for Stroke-Related Dysphagia and in Healthy Ageing. Dysphagia, 36(2), 281–292.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10129-8
Johnston, T. E., Keller, S., Denzer-Weiler, C., & Brown, L. (2021). A Clinical Practice Guideline for the Use of Ankle-Foot Orthoses and Functional Electrical Stimulation Post-Stroke. Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy: JNPT, 45(2), 112–196.
https://doi.org/10.1097/NPT.0000000000000347
Kiper, P., Szczudlik, A., Agostini, M., Opara, J., Nowobilski, R., Ventura, L., Tonin, P., & Turolla, A. (2018). Virtual Reality for Upper Limb Rehabilitation in Subacute and Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Archives of Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation, 99(5), 834–842.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2018.01.023
Lee, J. B., Kim, S. B., Lee, K. W., Lee, J. H., Park, J. G., & Lee, S. J. (2019). Combined Therapy With Functional Electrical Stimulation and Standing Frame in Stroke Patients. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine, 43(1), 96–105.
https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.1.96
Pozuelo-Carrascosa, D. P., Carmona-Torres, J. M., Laredo-Aguilera, J. A., Latorre-Román, P. Á., Párraga-Montilla, J. A., & Cobo-Cuenca, A. I. (2020). Effectiveness of Respiratory Muscle Training for Pulmonary Function and Walking Ability
in Patients with Stroke: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(15), 5356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155356
Veldema, J., & Jansen, P. (2020). Ergometer Training in Stroke Rehabilitation: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 101(4), 674–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2019.09.017