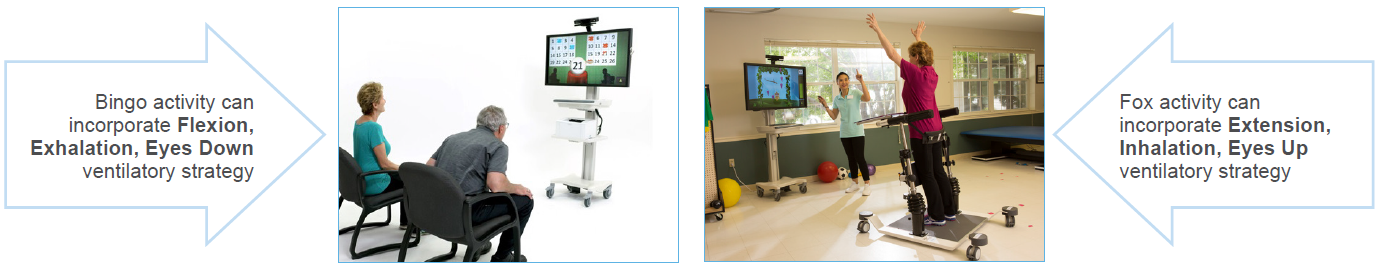
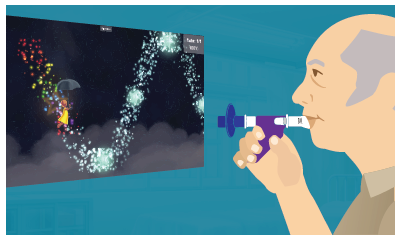
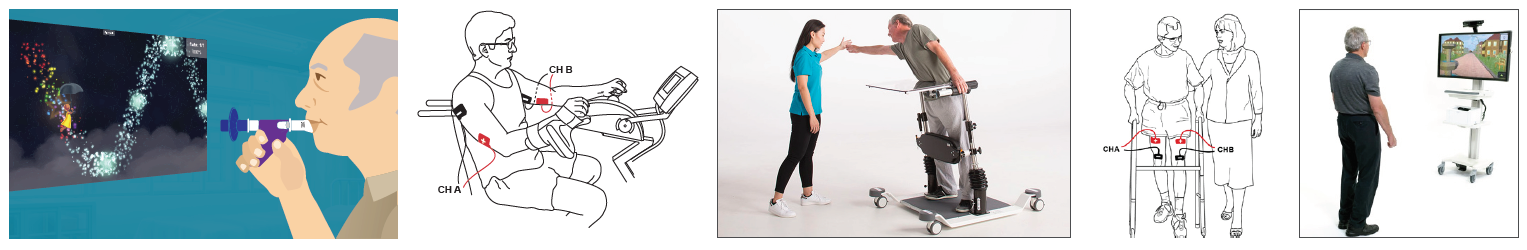
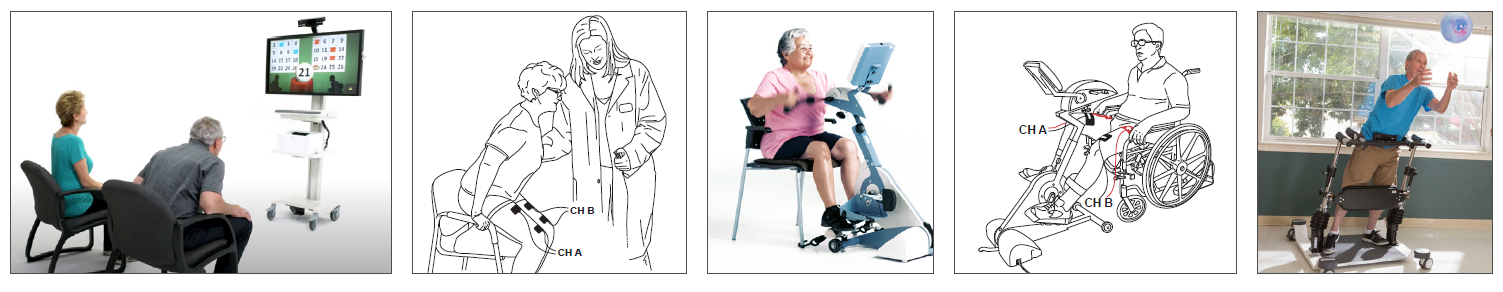
Individuals with cardiopulmonary conditions often present with dyspnea, severe weakness, poor endurance, limited mobility, and decreased activity tolerance. As their disease state progresses, their ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) declines, ultimately leading to a loss of independence. A therapy plan of care that includes breathing exercises, energy conservation techniques (e.g., paced activity, assistive device, task planning), and ventilatory strategies may improve the individual’s breathing and functional performance as well as help maintain independence.
Ventilatory Strategies for Cardiopulmonary Conditions
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Dementia Care With Advanced Rehabilitation Technology: Exercise
According to the CDC, dementia affects one’s ability to remember, think, and make decisions that impact daily activities and safety. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common type of dementia accounting for 60-80% of cases. As dementia progresses to increased levels of memory loss and confusion, the individual becomes more sedentary and frail. Rehabilitation in this population should be tailored to patient needs addressing cognition, strength, gait, balance, endurance, and function.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Interventions for Individuals with Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder often requiring therapy to address motor symptoms such as bradykinesia, rigidity, tremors, shuffling and freezing gait, poor postural control, and impaired balance. Exercise plays a key role in rehabilitation for this population with additional benefits being achieved by incorporating biophysical agents and advanced technologies. Research demonstrates that exercise improves motor skill performance, which may be enhanced with cognitive engagement through feedback, cueing, dual-tasking training, and motivation (Petzinger, et al., 2013).
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Virtual Reality in Fall Prevention
According to the CDC, more than one in four older adults fall each year. Falls may lead to fear of falling, decreased mobility, dependence, increased risk of future falls, and even death. The goal of a fall prevention and balance program is to decrease future falls and improve functional mobility, safety, and quality of life. Rehabilitation for those at risk of falling may include training for static and dynamic balance, gait, dual-task (DT) activity, and cognition which may be accomplished with virtual reality.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
Rehabilitation in Individuals with Long COVID
According to the CDC, in the U.S. there have been more than 33.9 million cases since January 2020. As many as 1 in 10 of those who develop COVID-19 exhibit new and prolonged symptoms lasting 12 weeks or longer. This is known as long COVID and occurs regardless of the severity of the acute illness. These individuals may have multisystem involvement with the most common symptoms after 6 months being fatigue, post-exertional symptom exacerbation (PESE), and problems with memory and concentration (brain fog). Therapists should screen for PESE, a worsening of symptoms typically 12 to 48 hours following even minimal cognitive, physical, emotional, or social activity that may last for days or weeks. (World Physiotherapy, 2021)
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Interdisciplinary Fall Prevention for Geriatrics
In a recent CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, Moreland & Lee (2021) analyzed 2018 U.S. data which revealed individuals 65 and older had 2.4 million emergency department visits and more than 700,000 hospitalizations due to unintentional injuries. Greater than 90% of these injuries were related to falls. This shows the importance of an effective interdisciplinary fall prevention and balance program for the geriatric population.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
Rehabilitation of Individuals Post-Stroke
According to the CDC, each year in the United States more than 795,000 people suffer a stroke and it is the leading cause of serious long-term disability. Individuals who suffer a stroke may have muscle weakness throughout the body including muscles of respiration and swallowing. They also may have compromised endurance, poor balance, and increased dependency with mobility and activities of daily living which greatly impact their quality of life.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Improving ADL Performance and Independence in Chronic Conditions
According to the CDC, 78% of adults over 55 in the U.S. have one or more chronic conditions. The ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) such as transfers, dressing, and bathing along with instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) such as shopping, cooking, and cleaning informs healthcare professionals regarding the individual’s level of independence. With chronic conditions such as COPD, chronic heart failure, stroke, and diabetes, individuals may have dyspnea, weakness, and poor aerobic capacity which in turn may lead to impaired ability to perform ADLs and IADLs.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Rehabilitation for Individuals with Pulmonary Conditions
Respiratory diseases are among the leading causes of death and disability in the United States. In 2019, chronic lower respiratory disease including asthma, but predominately chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), was the 4th leading cause of death and influenza and pneumonia the 9th leading cause of death (Kochanek et al., 2020). The ranking for 2020 will likely change due to COVID-19-related deaths at greater than 500,000.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Biophysical Agents and Advanced Technologies in the Rehabilitation of Patients with Heart Failure
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women in the United States with greater than 600,000 deaths attributed each year. Along with other conditions such as diabetes and obesity, heart disease may lead to heart failure which affects 6.2 million Americans per year (CDC, 2020).
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary