Individuals with cardiopulmonary conditions often present with dyspnea, severe weakness, poor endurance, limited mobility, and decreased activity tolerance. As their disease state progresses, their ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) declines, ultimately leading to a loss of independence. A therapy plan of care that includes breathing exercises, energy conservation techniques (e.g., paced activity, assistive device, task planning), and ventilatory strategies may improve the individual’s breathing and functional performance as well as help maintain independence.
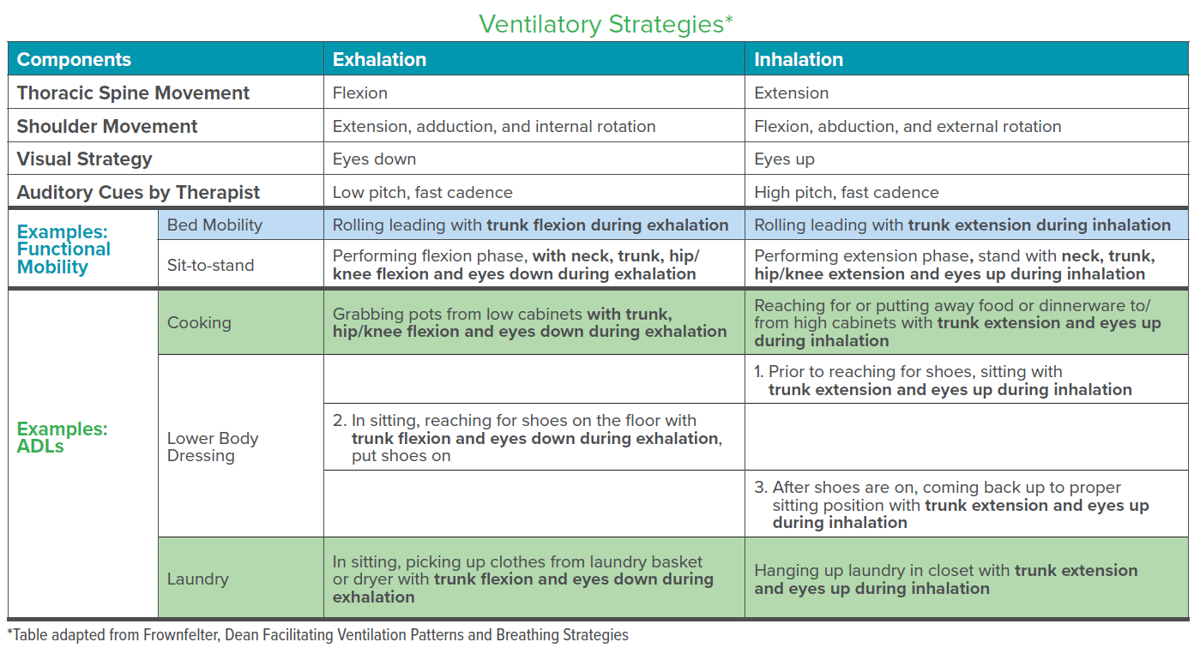
Ventilatory strategies (pairing breathing with movement) should be utilized if individuals inappropriately hold their breath or demonstrate shallow breathing during an activity. Actively incorporating breathing patterns with movement promotes better ventilation and facilitates improved task performance. Inhalation with trunk extension facilitates chest and rib expansion, and exhalation with trunk flexion facilitates abdominal and intercostal muscle activation. The addition of verbal cues with ventilatory strategies can even change passive exercise to dynamic exercise. (Frownfelter, 2015)
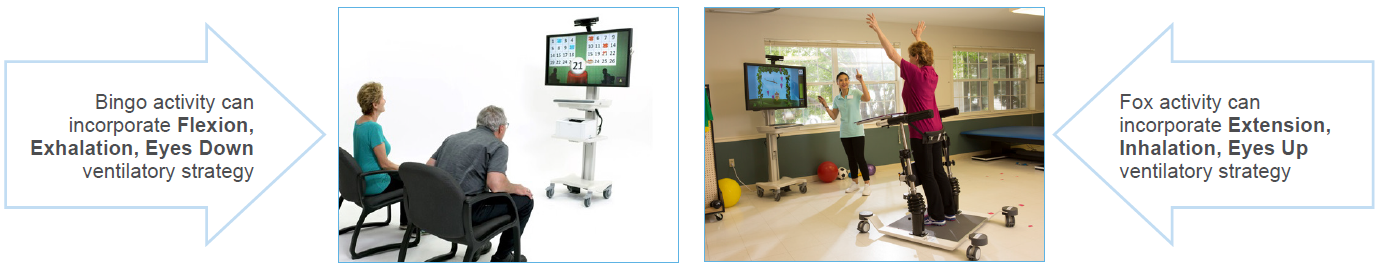
 OmniVR® engages and challenges cognitive and physical abilities in a virtual environment. Exercises can be performed in a seated or standing position and combined with ventilatory strategies depending on the individual’s ability and focus of the activity.
OmniVR® engages and challenges cognitive and physical abilities in a virtual environment. Exercises can be performed in a seated or standing position and combined with ventilatory strategies depending on the individual’s ability and focus of the activity.
References:
Frownfelter, D., Dean, E. (2015) Facilitating Ventilation Patterns and Breathing Strategies. In Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy (5th ed., Ch. 23). Elsevier.
https://clinicalgate.com/facilitating-ventilation-patterns-and-breathing-strategies/

