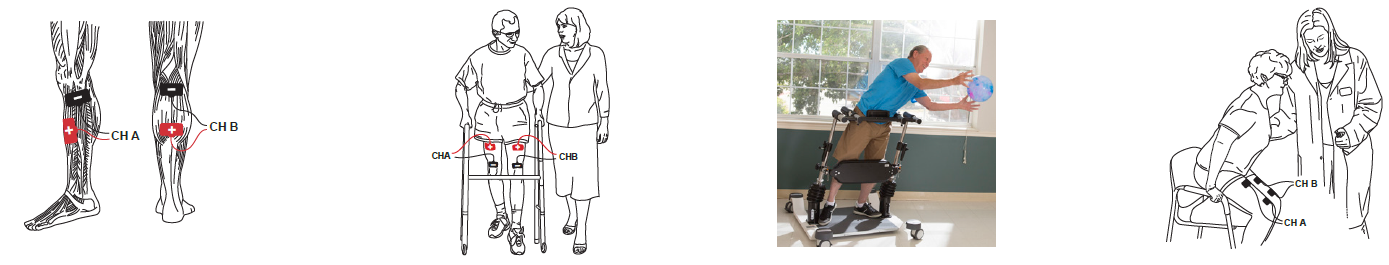
Muscle strength decline is associated with normal aging and may be accelerated by illness, disease, or injury. Decreased physical activity resulting from COVID-19 mitigation efforts is exacerbating the incidence of muscle disuse atrophy in older adults. Strength declines may lead to functional and mobility deficits with increased risk of falls, injury, or death. According to the CDC, each year three million adults are treated in emergency departments for injuries related to falls. By 2030 fall deaths are anticipated to rise to seven per hour. Accurate assessment of strength using validated tests and objective measures is crucial to creating an appropriate treatment plan and achieving outcomes that reduce fall risk.
Objective Tests and Measures: Strength Assessment and Treatment Guidance
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
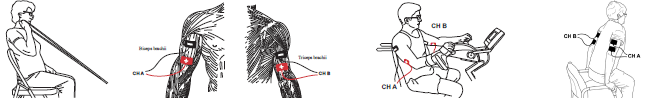
Cycling Exercise in Rehabilitation to Improve Coordination and Normalize Muscle Tone
Physical and occupational therapists treat many individuals who present with impaired coordination, motor control, balance and tone. These individuals may have a wide range of diagnoses, from neurologically involved, such as cerebral vascular accident (CVA) and Parkinson’s disease, to orthopedic involvement such as post-total knee replacement (TKR). The common goal of improving functional mobility and outcomes may be achieved by the addition of research-supported cycling and biophysical agents.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary, Neuro Rehab
The rehabilitation of patients with and recovering from COVID-19 is evolving and will be an integral part of therapy for the foreseeable future. The American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) developed a task force representing all academies and sections to identify core outcome measures to be used with all patients diagnosed with COVID-19 throughout care, across all settings. These outcome measures are to be used with patients having goals associated with five constructs; function, strength, endurance, cognition, and quality of life. (APTA, 2020)
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Diaphragmatic Breathing Exercise and Patterned Electrical Neuromuscular Stimulation (PENS)
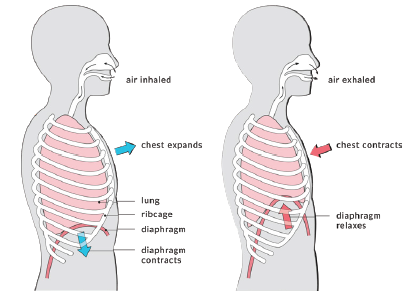
Diaphragmatic breathing helps individuals use their diaphragm correctly while breathing and enhances oxygen exchange (Cleveland Clinic, 2020). With age, stress, poor posture, and illness breathing changes and becomes shallow with increased reliance on accessory muscles. Implementing diaphragmatic breathing may help improve oxygen delivery throughout the body, use less effort and energy to breathe, and decrease overall oxygen demand.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
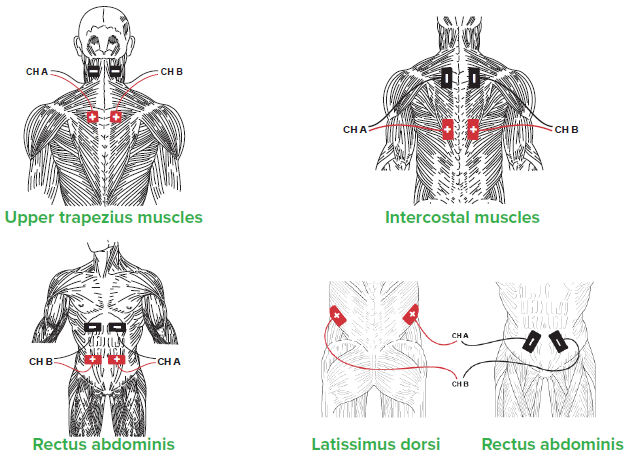
Improving Activation of Accessory Respiratory Muscles with NMES
Primary respiratory muscles during normal quiet breathing include the diaphragm and external intercostals. Accessory muscles of respiration assist the primary muscles when the chest is not expanding or contracting effectively to meet ventilation demands. Increased age, stress, poor posture, COPD, pneumonia, and illness are conditions that negatively impact proper oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in the lungs.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
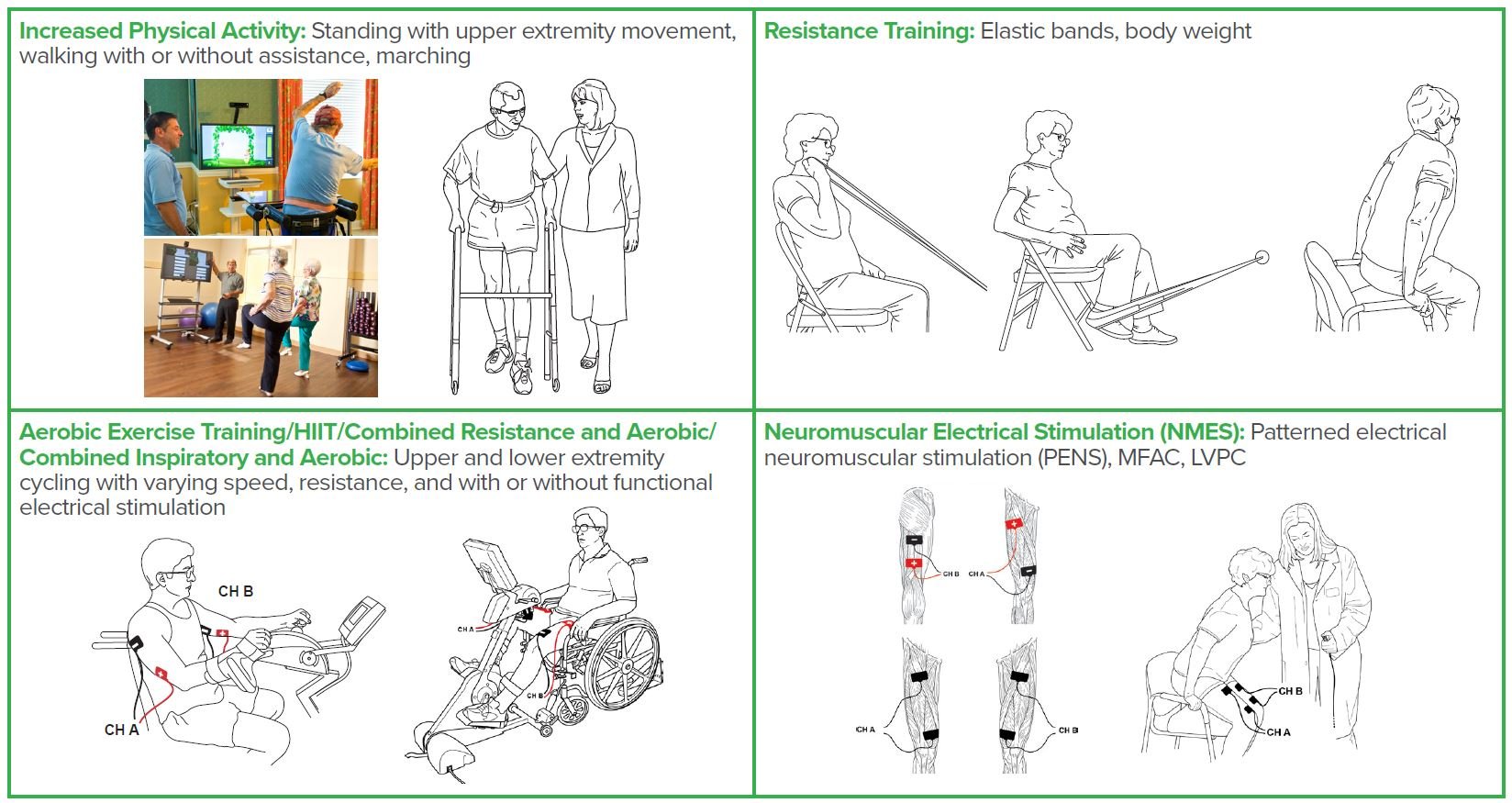
Rehabilitation for Severe Deconditioning Using Advanced Technology and Electrical Stimulation
Individuals who present with a compromised pulmonary system, are acutely ill, or hospitalized for extended periods may become deconditioned or develop hospital-acquired muscle weakness, among other deleterious effects. Even healthy individuals may become deconditioned and frail if they decrease their activity level due to social distancing and limiting time outside their room or home.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
Infection control and patient safety are top priorities in healthcare. This document reviews low-level and intermediate-level infection control procedures for use with ACP technology to ensure the safety of healthcare providers and patients.
Topics: Clinical Tip
Heart Failure Clinical Practice Guidelines Therapy Recommendations
Approximately 6.5 million adults in the United States have heart failure. Heart failure (previously referred to as chronic heart failure or CHF) occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood throughout the body to meet the requirements of other organs and muscles. This results in a wide variety of symptoms and functional impairments which may result in hospitalization, re-hospitalization, and death. In 2017, heart failure contributed to 1 in 8 deaths. (CDC, 2020)
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary
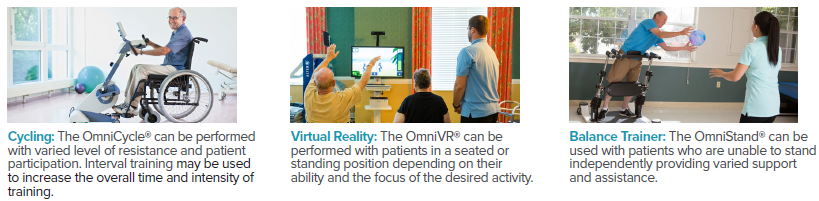
Over the past several years, the body of evidence on the effectiveness of virtual reality (VR) in rehabilitation has significantly expanded. VR has been studied for a variety of diagnoses including stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, dementia, burns, pain, and total knee arthroplasty. VR helps enhance patient involvement and motivation while increasing the repetitions and duration of exercise. Benefits addressing ADL performance, balance, gait, pain, and cognition have been reported.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Pain Management, Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary, Orthopedic, Neuro Rehab
Hypertonia is defined as excessive muscle tone which leads to stiffness with movement or inability to move a joint and often occurs with neurological conditions such as upper motor neuron lesions (CP, CVA, TBI, SCI, MS) and basal ganglia disorders (PD, Huntington
disease, Dystonia). While the terms spasticity and hypertonia are often used interchangeably, spasticity is actually a subtype of hypertonia in which muscle tone is increased by the speed of joint movement. (NIH, 2019)
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab