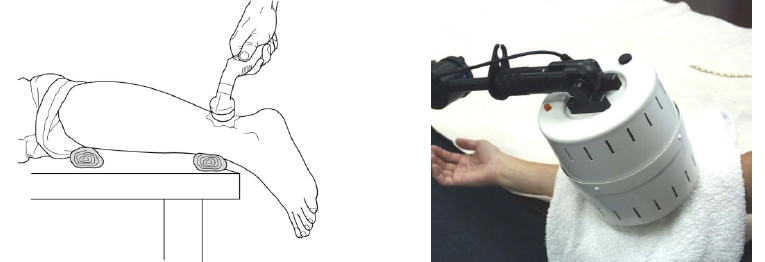
Range of motion (ROM) deficits may affect an individual’s ability to move, care for themselves, or perform typical daily activities including self-feeding, walking, and dressing. Decreased ROM is a common deficit addressed regularly by rehab professionals in all settings. Contractures arise from shortened muscle or other joint structure restrictions, leading to reduction in mobility and deformity with resultant reduced function.
• Prevalence of contractures in nursing homes is estimated at 55% with significant functional and medical consequences. (Offenbächer, 2014)
• Patients who are immobilized for a prolonged period are at risk of developing joint contractures, which often affect functional outcomes. (Born, 2017)
Topics: Clinical Tip, Orthopedic, Neuro Rehab
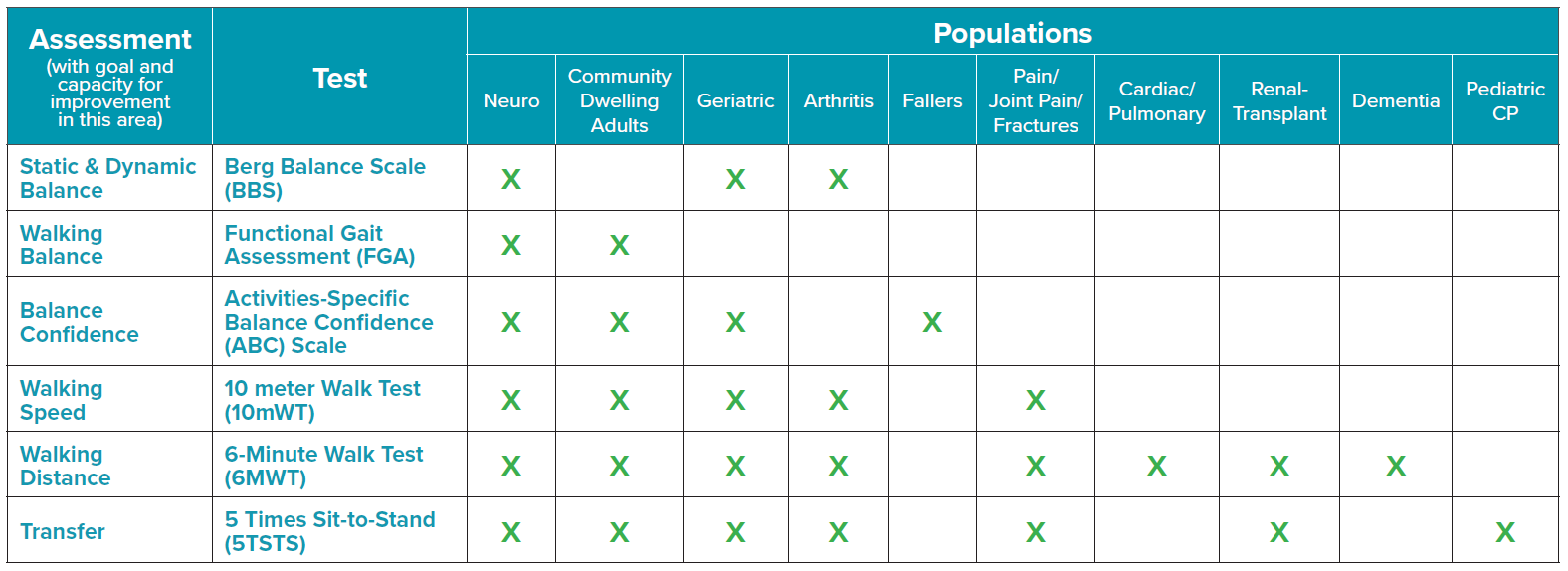
The use of outcome measures has become the standard of care to objectively assess changes in function, quantify clinical observations, enhance interdisciplinary communication, and examine intervention effectiveness at the patient and practice levels. Inconsistent use of outcome measures remains an issue due to difficulty identifying the most suitable measures based on patient diagnosis, acuity of condition, or practice setting.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
Per the American Physical Therapy Association’s (APTA) “Defensible Documentation Tips” resource¹, the top 10 payer complaints about documentation (reasons for denials) include:
Topics: Clinical Tip
Using Electrical Stimulation to Manage Complications of Diabetes
It is estimated that over 30 million individuals (9.4%) in the US population has diabetes, while more than one in four do not know they have the disease. A staggering 84.1 million adults have pre-diabetes and, of these individuals, 9 out of 10 are unaware of the condition. Diabetes affects multiple parts of the body and causes many complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney dysfunction, diabetic neuropathy, orthopedic problems, gum disease, and eye disease. Managing blood glucose levels, a healthy lifestyle and physical activity can help prevent these complications.¹
Topics: Pain Management, Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
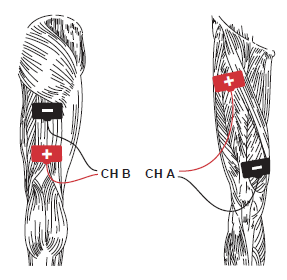
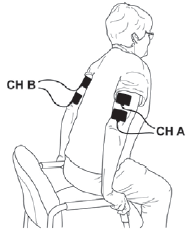
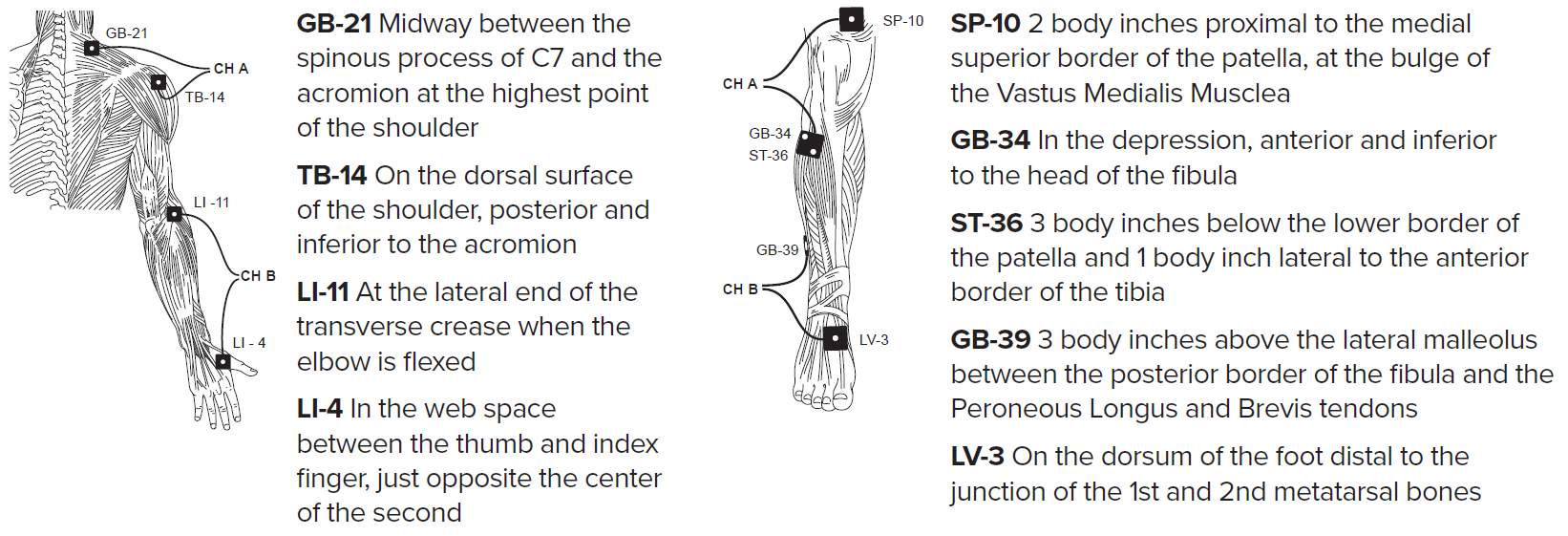
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) Using Medium Frequency Alternating Current (MFAC) Hand Control
ACP’s MFAC Hand Control protocol provides for electrical stimulation-assisted muscle contraction to assist with the development of functional movement of superficial and deep muscles. To maximize the therapeutic effect of the intervention, the electrical stimulation delivered by the MFAC Hand Control protocol should be set to elicit a grade 3-5 muscle contraction and should be administered along with a strong volitional contraction by the patient.
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
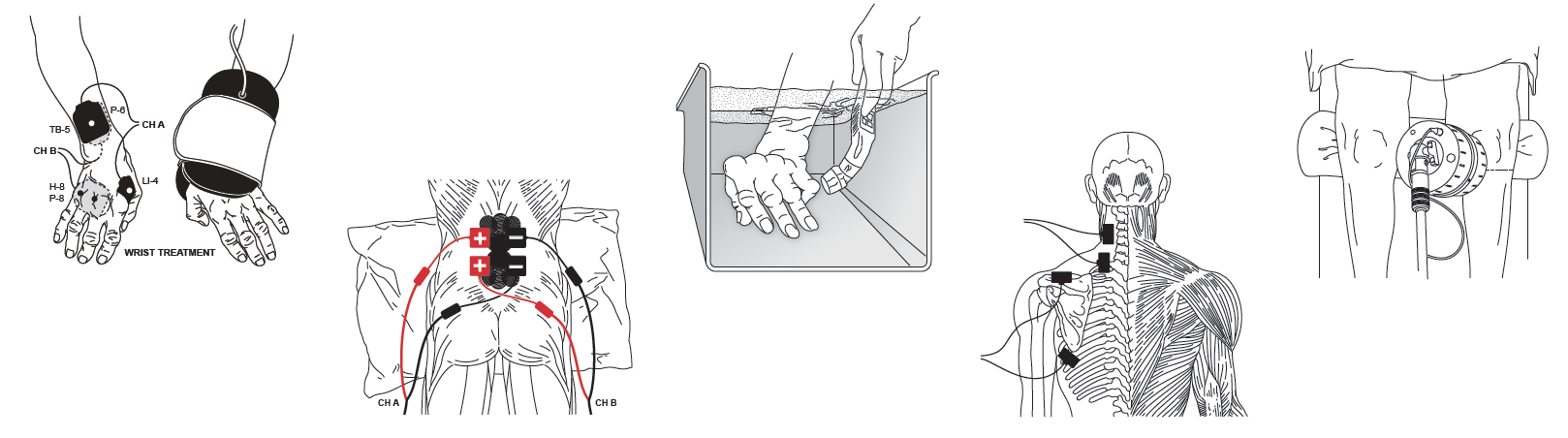
Electrical Stimulation Intervention to Treat Stroke Related Impairments
Cerebral vascular accident (CVA), or stroke, affects 795,000 individuals each year and is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States, killing 140,000. Approximately 87% of all strokes are the ischemic-type. Additionally, it is the leading cause of serious long-term disability. Individuals who suffer stroke often have communication challenges, dysphagia, pain, edema, depression, limitations in mobility, and impaired functional ability.1,2
Topics: Clinical Tip, Neuro Rehab
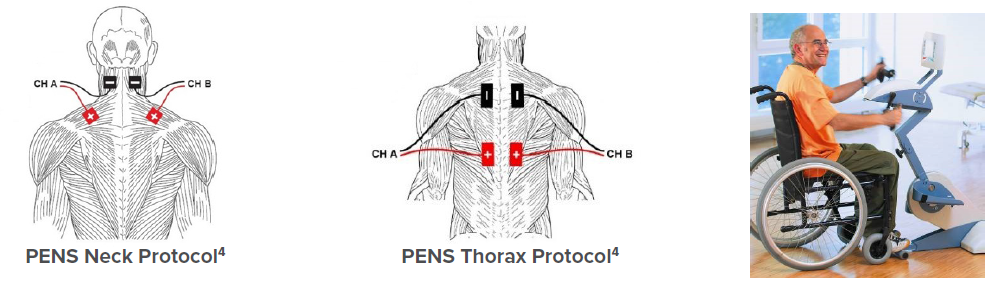
Biophysical Agent Alternatives to Opioids for Pain Management
Opioids are commonly prescribed for acute and chronic pain, including after surgeries such as THR, TKR, and ORIF. Opioids have numerous side effects and a high potential for misuse. Over-reliance on opioids for acute and chronic pain management has led to alarming trends across the United States, including a record number of people developing opioid use disorders, overdosing on opioids, and dying from overdoses. From 2015 to 2017, the annual number of opioid-related deaths rose 44% from 33,000 to 47,600.¹
Topics: Pain Management, Clinical Tip
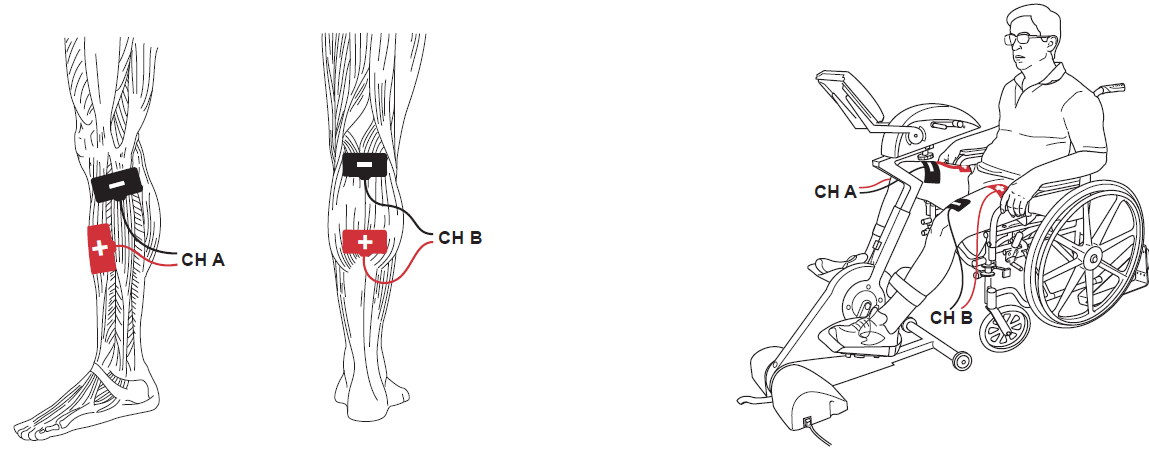
Using ACP’s Fall Prevention and Balance Program to Reduce Falls and Improve Patient Outcomes
According to the CDC, falls are not only a serious health risk, they carry a high economic burden as well. For older adults in the US, fall mortality rates have increased by 30% from 2007 to 2016. In 2015, the total medical cost for falls was more than $50 billion with Medicare and Medicaid accounting for 75% of these costs. The statistics related to falls are astounding. Each year:¹
• Three million older adults are treated in emergency departments for fall injuries
• 800,000+ patients are hospitalized due to a fall-related injury, most often head injury or hip fracture
• A typical nursing home with 100 residents reports about 100-200 falls
– 35% of injuries due to falls occur in residents who do not ambulate
• 24% (most common cause) of falls among elderly nursing home residents are due to muscle weakness and gait problems, whereas 16-27%, on average, are due to environmental hazards
Topics: Fall Prevention & Balance, Clinical Tip
Proper trunk positioning is an essential component of optimal aerobic capacity training. Poor positioning of the head, neck, shoulders, trunk, and pelvis during aerobic exercise may compromise an individual’s ability to reach optimal functional outcomes.
Topics: Clinical Tip, Cardiopulmonary, Orthopedic
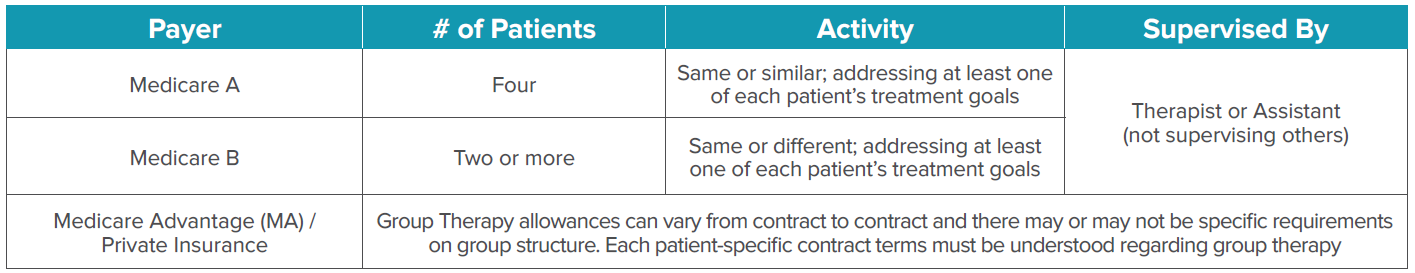
Clinical Efficacy and Treatment Efficiency with Group Therapy
Increasing emphasis on the value of care over the volume of care provides opportunity to incorporate different therapy delivery modes. Therapy delivered in a group format offers benefits over traditional one-on-one therapy that include increased socialization, independence with exercise, and improved transference of learning.
Topics: Clinical Tip